NXP IMX95LPD5EVK-19CM board TEVS Camera Usage Guide

🚀 Introduction
This article guides you how to get started using TechNexion camera modules on NXP IMX95LPD5EVK-19CM board.
📸 Supported Camera Modules
| Camera Series | Products |
|---|---|
| TEVS | TEVS-AR0144 TEVS-AR0145 TEVS-AR0234 TEVS-AR0521 TEVS-AR0522 TEVS-AR0821 TEVS-AR0822 TEVS-AR1335 |
🔧 Hardware Setup Instructions
Connect the Adapter Board and Camera Cable
To set up TechNexion camera, connect the adapter board and camera cable to the MIPI CSI port on the EVK board.
🧰 Camera Installation Instructions
We provide some methods to install camera driver and device tree blobs. Depending on your needs, you can choose the most suitable method. If you are new to this, we recommend starting with Method 1. If you want to customized your Yocto project or Linux kernel, you can try Method 2 or Method 3. If you have a custom Linux kernel and device tree, you can try Method 4.
Method 1 - Using TechNexion Pre-built image
Prepare Yocto demo image for testing TechNexion camera
To test TechNexion TEVS Series cameras, you need a demo image that includes the required Device Tree Blobs (DTBs) and camera drivers.
Download and Select the Correct Image for Your EVK
Prebuilt demo images can be available for download via TechNexion's server.
Download Link:
🔗 Supported Release List (Instructions for IMX95LPD5EVK-19CM)
Flashing the Image
You can flash the image to an SD Card using the following methods:
Make sure your EVK board is set to boot from SD card.
Refer to the official NXP guide 🔗 i.MX 95 LPD5 EVK Quick Start Guide
- For Windows Users
- For Linux Users
Method 2 - Build Yocto image with TechNexion BSP
TechNexion supports building a Yocto-based Linux image tailored for camera modules using the following kernel and branch.
If you are using prebuilt demo image, you can skip this section. Please refer to 📸 Camera Testing Instructions section for camera testing steps.
Supported Linux Kernel
| Linux Kernel Version | Yocto Branch |
|---|---|
| 6.6.52 | tn-imx_6.6.52_2.2.0-stable |
Source and Build Instructions
🔗 Fetch Yocto source
📖 Build Yocto (Instructions for IMX95LPD5EVK-19CM)
Method 3 - Build Linux kernel with TechNexion source code
Clone the Kernel Source
Fetch and compile Linux kernel.
- Host OS: Ubuntu 20.04
- Toolchain:
aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc 9.4.0
Install cross-compile & dependency tools.
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt install -y gcc-aarch64-linux-gnu libncurses-dev libssl-dev bison flex git make
Clone the Kernel Source
$ git clone https://github.com/TechNexion/linux-tn-imx.git -b tn-imx_6.6.52_2.2.0-stable
Set cross-compile environment & the kernel config.
$ export ARCH=arm64
$ export CROSS_COMPILE=/usr/bin/aarch64-linux-gnu-
$ cd linux-tn-imx
~/linux-tn-imx$ make imx_v8_defconfig
Compile the kernel & module driver.
# compile kernel
~/linux-tn-imx$ make -j$(nproc)
# create kernel module folder
~/linux-tn-imx$ mkdir -p ./modules
# compile module driver
~/linux-tn-imx$ rm -rf ./modules/*
~/linux-tn-imx$ make INSTALL_MOD_PATH=./modules modules_install
Change kernel Image, DTB & modules.
~/linux-tn-imx/$ cp arch/arm64/boot/Image <mount_folder>/boot/Image
~/linux-tn-imx/$ cp arch/arm64/boot/dts/freescale/imx95-19x19-evk-tevs-tev-nxp.dts <mount_folder>/boot/
~/linux-tn-imx/$ sudo cp -r ./modules/lib/modules/* <mount_folder>/root/lib/modules/
Method 4 - Build custom Linux kernel with camera driver
-
Download the camera driver and device tree blobs.
$ git clone https://github.com/TechNexion-Vision/nxp_evk_camera.git -b tn-imx_6.6.52_2.2.0-stable -
Copy to your kernel source code.
$ cd nxp_evk_camera/
~/nxp_evk_camera$ cp -r driver/media/i2c/tevs/ <fetch_kernel_folder>/driver/media/i2c/
~/nxp_evk_camera$ cp arch/arm64/boot/dts/freescale/imx95-19x19-evk-tevs-tev-nxp.dts<fetch_kernel_folder>/arch/arm64/boot/dts/freescale/ -
Modify makefile to add driver.
$ cd <fetch_kernel_folder>/driver/media/i2c/
~/<fetch_kernel_folder>/driver/media/i2c/$ vi MakefileAdd this line in Makefile.
obj-$(CONFIG_VIDEO_TEVS) += tevs/
you can refer to linux-tn-imx/drivers/media/i2c/Makefile
-
Modify Kconfig to add camera config.
~/<fetch_kernel_folder>/driver/media/i2c/$ vi KconfigAdd this part under "Camera sensor devices" menu in Kconfig.
config VIDEO_TEVS
tristate "TechNexion TEVS sensor support"
depends on OF
depends on GPIOLIB && I2C && VIDEO_V4L2_SUBDEV_API
depends on MEDIA_CAMERA_SUPPORT
select V4L2_FWNODE
default y
help
This is a Video4Linux2 sensor driver for the TechNexion
TEVS camera sensor with a MIPI CSI-2 interface.
you can refer to linux-tn-imx/drivers/media/i2c/Kconfig
-
Modify makefile to add device tree.
$ cd <fetch_kernel_folder>/arch/arm64/boot/dts/freescale/
~/<fatch_kernel_folder>/arch/arm64/boot/dts/freescale/$ vi MakefileAdd this line in Makefile.
imx95-19x19-evk-tevs-dtbs := imx95-19x19-evk.dtb imx95-19x19-evk-tevs-tev-nxp.dtbo
dtb-$(CONFIG_ARCH_MXC) += imx95-19x19-evk-tevs.dtb
you can refer to linux-tn-imx/arch/arm64/boot/dts/freescale/Makefile
-
Compile the kernel & module driver.
Finally, you can start compiling your new Image files, then copy and replace the Image files in the SD card.
📸 Camera Testing Instructions
Specify Camera DTBO in U-Boot
-
Connect the debug console cable to the baseboard (via USB-C).
-
Power on the board and interrupt the boot process. Keep pressing
Enterwhen the following message appears:Hit any key to stop autoboot: -
Specify the appropriate device tree for your camera using the
fdtfileenvironment variable in U-Boot:
u-boot=> setenv fdtfile imx95-19x19-evk-tevs-tev-nxp.dtb
- Save and continue the boot process:
u-boot=> saveenv
u-boot=> boot
Setup the media controller before camera streaming
To verify that the camera has been properly connected and linked, use the media-ctl command:
$ media-ctl -p
Get the media controller information as follows.
Media controller API version 6.6.23
Media device information
\------------------------
driver mxc-isi
model FSL Capture Media Device
serial
bus info platform:4ad50000.isi
hw revision 0x0
driver version 6.6.23
Device topology
\- entity 1: crossbar (13 pads, 9 links, 8 routes)
type V4L2 subdev subtype Unknown flags 0
device node name /dev/v4l-subdev0
routes:
2/0 -> 5/0 [ACTIVE]
2/0 -> 6/0 [ACTIVE]
2/0 -> 7/0 [ACTIVE]
2/0 -> 8/0 [ACTIVE]
2/0 -> 9/0 [ACTIVE]
2/0 -> 10/0 [ACTIVE]
2/0 -> 11/0 [ACTIVE]
2/0 -> 12/0 [ACTIVE]
pad0: Sink
pad1: Sink
pad2: Sink
[stream:0 fmt:UYVY8_1X16/1920x1080 field:none colorspace:srgb xfer:srgb ycbcr:601 quantization:lim-range]
<\- "4ac10000.syscon:formatter@20":1 [ENABLED,IMMUTABLE]
pad3: Sink
pad4: Sink
pad5: Source
[stream:0 fmt:UYVY8_1X16/1920x1080 field:none colorspace:srgb xfer:srgb ycbcr:601 quantization:lim-range]
-> "mxc_isi.0":0 [ENABLED,IMMUTABLE]
…
\- entity 15: mxc_isi.0 (2 pads, 2 links, 0 routes)
type V4L2 subdev subtype Unknown flags 0
device node name /dev/v4l-subdev1
pad0: Sink
[stream:0 fmt:UYVY8_1X16/1920x1080 field:none colorspace:jpeg xfer:srgb ycbcr:601 quantization:full-range
compose.bounds:(0,0)/1920x1080
compose:(0,0)/1920x1080]
<\- "crossbar":5 [ENABLED,IMMUTABLE]
pad1: Source
[stream:0 fmt:YUV8_1X24/1920x1080 field:none colorspace:jpeg xfer:srgb ycbcr:601 quantization:full-range
crop.bounds:(0,0)/1920x1080
crop:(0,0)/1920x1080]
-> "mxc_isi.0.capture":0 [ENABLED,IMMUTABLE]
\- entity 18: mxc_isi.0.capture (1 pad, 1 link)
type Node subtype V4L flags 0
device node name /dev/video0
pad0: Sink
<\- "mxc_isi.0":1 [ENABLED,IMMUTABLE]
…
\- entity 103: 4ac10000.syscon:formatter@20 (2 pads, 2 links, 1 route)
type V4L2 subdev subtype Unknown flags 0
device node name /dev/v4l-subdev9
routes:
0/0 -> 1/0 [ACTIVE]
pad0: Sink
[stream:0 fmt:UYVY8_1X16/1920x1080 field:none colorspace:smpte170m xfer:709 ycbcr:601 quantization:lim-range]
<\- "csidev-4ad30000.csi":1 [ENABLED,IMMUTABLE]
pad1: Source
[stream:0 fmt:UYVY8_1X16/1920x1080 field:none colorspace:smpte170m xfer:709 ycbcr:601 quantization:lim-range]
-> "crossbar":2 [ENABLED,IMMUTABLE]
\- entity 108: csidev-4ad30000.csi (2 pads, 2 links, 1 route)
type V4L2 subdev subtype Unknown flags 0
device node name /dev/v4l-subdev10
routes:
0/0 -> 1/0 [ACTIVE]
pad0: Sink
[stream:0 fmt:UYVY8_1X16/1920x1080 field:none colorspace:smpte170m xfer:709 ycbcr:601 quantization:lim-range]
<\- "tevs 2-0048":0 []
pad1: Source
[stream:0 fmt:UYVY8_1X16/1920x1080 field:none colorspace:smpte170m xfer:709 ycbcr:601 quantization:lim-range]
-> "4ac10000.syscon:formatter@20":0 [ENABLED,IMMUTABLE]
\- entity 113: tevs 2-0048 (1 pad, 1 link, 0 routes)
type V4L2 subdev subtype Sensor flags 0
device node name /dev/v4l-subdev11
pad0: Source
[stream:0 fmt:UYVY8_1X16/640x480@1/60 field:none colorspace:srgb xfer:srgb ycbcr:601 quantization:full-range
crop.bounds:(0,0)/640x480
crop:(0,0)/640x480]
-> "csidev-4ad30000.csi":0 []
Transfer to image that will be easier to understand.
$ media-ctl --print-dot > graph.dot
$ dot -Tpng graph.dot > graph.png
# if you don't have tool, you need to install it as follows.
# sudo apt-get install -y graphviz
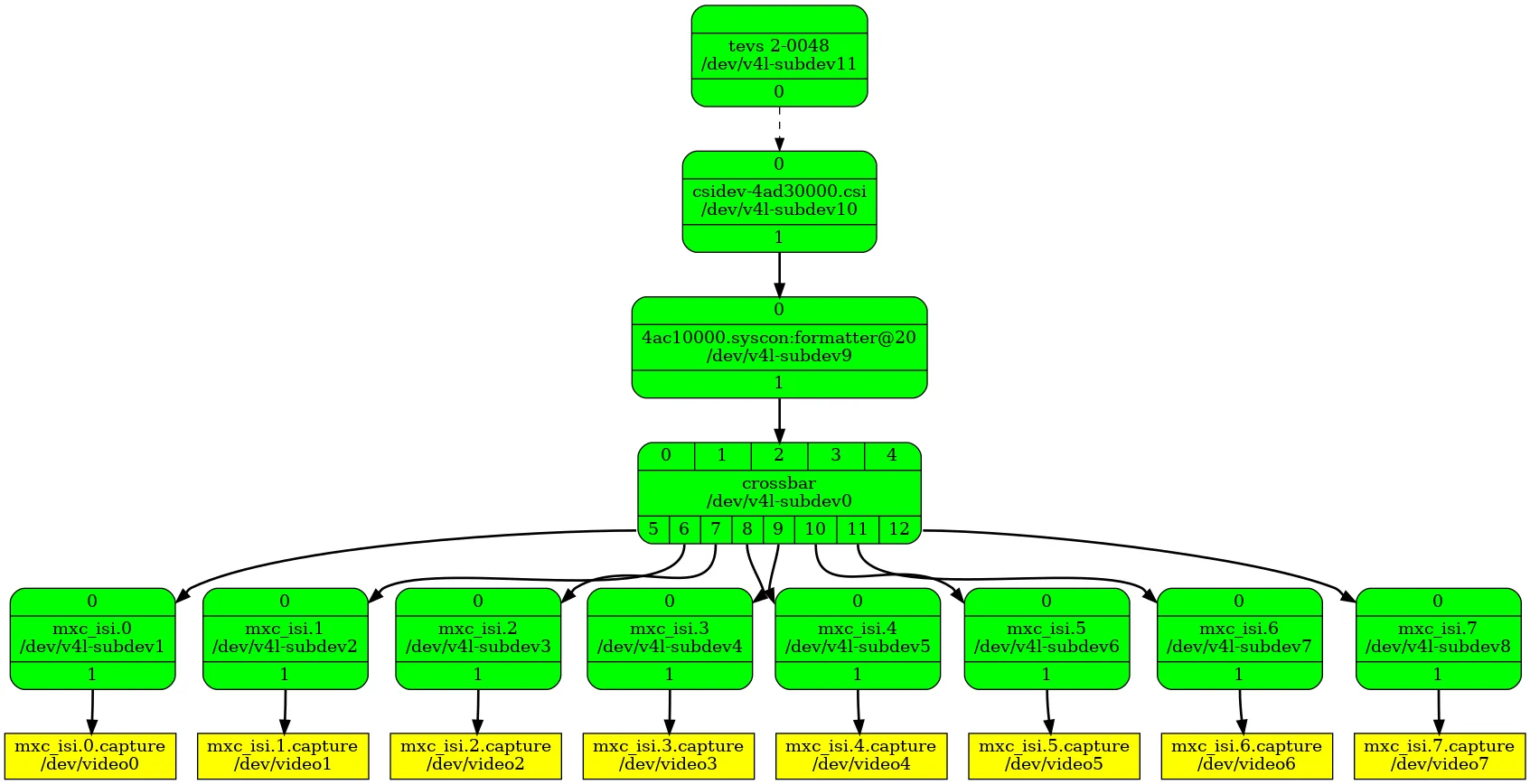
Modify the route through the “crossbar” and only keep the channel of video0.
$ media-ctl -R "'crossbar' [2/0 -> 5/0 [1], 2/0 -> 6/0 [0], 2/0 -> 7/0 [0], 2/0 -> 8/0 [0], 2/0 -> 9/0 [0], 2/0 -> 10/0 [0], 2/0 -> 11/0 [0], 2/0 -> 12/0 [0]]"
Enable the link between TEVS and CSI device.
$ media-ctl -l "'tevs 2-0048':0 -> 'csidev-4ad30000.csi':0 [1]"
You can list camera formats, resolutions and frame interval via v4l2 control command.
# formats
$ v4l2-ctl -d /dev/v4l-subdev11 --list-subdev-mbus-codes
ioctl: VIDIOC_SUBDEV_ENUM_MBUS_CODE (pad=0)
0x200f: MEDIA_BUS_FMT_UYVY8_1X16
# resolutions
$ v4l2-ctl -d /dev/v4l-subdev11 --list-subdev-framesize code=0x200f
ioctl: VIDIOC_SUBDEV_ENUM_FRAME_SIZE (pad=0)
Size Range: 640x480 - 640x480
Size Range: 1280x720 - 1280x720
Size Range: 1280x800 - 1280x800
# frame interval of resolution
$ v4l2-ctl -d /dev/v4l-subdev11 --list-subdev-frameintervals width=640,height=480,code=0x200f
ioctl: VIDIOC_SUBDEV_ENUM_FRAME_INTERVAL (pad=0)
Interval: 0.017s (60.000 fps)
$ v4l2-ctl -d /dev/v4l-subdev11 --list-subdev-frameintervals width=1280,height=720,code=0x200f
ioctl: VIDIOC_SUBDEV_ENUM_FRAME_INTERVAL (pad=0)
Interval: 0.017s (60.000 fps)
$ v4l2-ctl -d /dev/v4l-subdev11 --list-subdev-frameintervals width=1280,height=800,code=0x200f
ioctl: VIDIOC_SUBDEV_ENUM_FRAME_INTERVAL (pad=0)
Interval: 0.017s (60.000 fps)
Set the media controller resolution to 1280×720.
$ media-ctl -V "'crossbar':2 [fmt:UYVY8_1X16/1280x720 field:none colorspace:srgb xfer:srgb ycbcr:601]"
$ media-ctl -V "'mxc_isi.0':0 [fmt:UYVY8_1X16/1280x720 field:none colorspace:srgb xfer:srgb ycbcr:601]"
$ media-ctl -V "'4ac10000.syscon:formatter@20':0 [fmt:UYVY8_1X16/1280x720 field:none colorspace:srgb xfer:srgb ycbcr:601]"
$ media-ctl -V "'csidev-4ad30000.csi':0 [fmt:UYVY8_1X16/1280x720 field:none colorspace:srgb xfer:srgb ycbcr:601]"
$ media-ctl -V "'tevs 2-0048':0 [fmt:UYVY8_1X16/1280x720 field:none colorspace:srgb xfer:srgb ycbcr:601]"
🎥 Start Camera Video Stream via GStreamer
Launch GStreamer Pipeline
Specify the capture device you just get and start gstreamer to get video stream on screen.
$ gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src device=/dev/video0 ! "video/x-raw, format=YUY2, width=1280, height=720" ! waylandsink sync=false
🚨 Troubleshooting
Boot up NXP IMX95LPD5EVK-19CM and check initialization of TEVS driver. If it shows below messages, the driver is initialized correctly.
$ dmesg -t | grep tevs
tevs 1-0048: tevs_probe() device node: tevs@48
tevs 1-0048: Version:24.9.0.1
tevs 1-0048: Product:TEVS-AR0234, HeaderVer:3, MIPI_Rate:800
tevs 1-0048: probe success